Recognizing the Value of Foam Control in Food and Beverage Processing
Recognizing the Value of Foam Control in Food and Beverage Processing
Blog Article
Efficient Approaches for Accomplishing Optimal Foam Control in Chemical Production
Efficient foam control is an important facet of chemical manufacturing that can dramatically affect production performance and item top quality. By understanding the systems of foam development and selecting ideal anti-foaming representatives, producers can take proactive actions to minimize excessive foam.
Recognizing Foam Development
Surfactants, or surface-active agents, minimize the surface stress of the fluid, helping with bubble stability and advertising foam generation. In addition, agitation or mixing processes can boost bubble formation, commonly intensifying foam concerns. The qualities of the liquid tool, including thickness and thickness, additional influence foam habits; for example, more viscous fluids tend to catch air better, causing increased foam security.
Understanding these essential aspects of foam formation is crucial for effective foam control in chemical manufacturing. By acknowledging the problems that promote foam growth, makers can apply targeted strategies to alleviate its negative results, consequently maximizing manufacturing procedures and guaranteeing consistent item top quality. This fundamental knowledge is essential before discovering details methods for managing foam in commercial setups.
Option of Anti-Foaming Representatives
When choosing anti-foaming agents, it is necessary to consider the particular characteristics of the chemical process and the sort of foam being generated (Foam Control). Different factors affect the performance of an anti-foaming representative, including its chemical make-up, temperature stability, and compatibility with various other procedure products
Silicone-based anti-foams are commonly utilized because of their high effectiveness and wide temperature level range. They work by reducing surface tension, enabling the foam bubbles to integrate and break even more quickly. Nonetheless, they may not be suitable for all applications, especially those including sensitive formulas where silicone contamination is a worry.
On the various other hand, non-silicone agents, such as mineral oils or natural substances, can be helpful in particular scenarios, especially when silicone residues are unfavorable. These agents often tend to be less efficient at higher temperatures however can offer efficient foam control in other conditions.
Additionally, recognizing the foam's origin-- whether it occurs from oygenation, frustration, or chain reactions-- overviews the choice procedure. Testing under real operating problems is vital to ensure that the chosen anti-foaming representative fulfills the special requirements of the chemical production procedure efficiently.
Refine Optimization Techniques
Efficient foam control is an essential element of maximizing chemical manufacturing procedures. To improve efficiency and minimize production prices, makers have to implement targeted process optimization strategies. One crucial technique includes changing mixing rates and configurations. By fine-tuning these criteria, operators can minimize turbulence, consequently decreasing foam development throughout mixing.
In addition, regulating temperature level and stress within the system can significantly influence foam generation. Decreasing the temperature might lower the volatility of particular parts, bring about decreased foam. Maintaining optimum stress degrees assists in minimizing extreme gas release, which adds to foam stability.
One more efficient strategy is the tactical addition of anti-foaming agents at critical points of the procedure. Careful timing and dose can make sure that these representatives properly reduce foam without interrupting various other procedure criteria.
In addition, incorporating a systematic evaluation of resources properties can aid recognize inherently lathering materials, permitting preemptive procedures. Carrying out regular audits and process evaluations can expose ineffectiveness and locations for improvement, allowing continual optimization of foam control methods.
Surveillance and Control Equipment
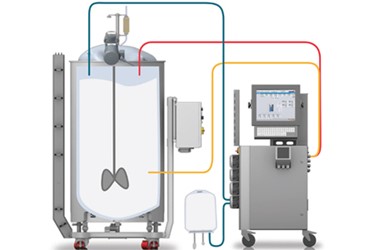
Monitoring and control systems play a critical function in maintaining ideal foam management throughout the chemical production procedure. These systems are necessary for real-time observation and adjustment of foam degrees, ensuring that production efficiency is taken full advantage of while lessening interruptions triggered by too much foam formation.
Advanced sensing units and instrumentation are used to find foam thickness and height, giving crucial information that educates control formulas. This data-driven strategy allows for the timely application of antifoaming representatives, making certain that foam degrees remain within appropriate restrictions. By incorporating tracking systems with procedure control software, makers can carry out computerized feedbacks to foam fluctuations, reducing the requirement for hands-on treatment and improving operational uniformity.
Additionally, the assimilation of equipment learning and predictive analytics into keeping track of systems can promote aggressive foam administration. By analyzing historic foam data and functional criteria, these systems can forecast foam generation patterns and suggest preemptive actions. Normal calibration and maintenance of monitoring tools are vital to guarantee precision and reliability in foam detection.
Eventually, effective tracking and control systems are important for optimizing foam control, promoting safety, and enhancing general productivity in chemical production settings.

Situation Researches and Finest Practices
Real-world applications of surveillance and control systems highlight the significance of from this source foam management in chemical manufacturing. A significant instance study entails a large pharmaceutical maker that applied an automated foam detection system.
One more excellent case comes from a petrochemical firm that took on a mix of antifoam agents and procedure optimization techniques. By analyzing foam generation patterns, the company tailored its antifoam dosage, resulting in a 25% reduction in chemical use and considerable expense savings. This targeted method not only minimized foam disturbance yet likewise improved the general security of the production process.

Conclusion
Finally, accomplishing optimum foam control in chemical manufacturing demands an extensive approach including the choice of suitable anti-foaming representatives, execution of procedure optimization strategies, and the combination of advanced tracking systems. Routine audits and training further improve the performance of these approaches, fostering a culture of continual renovation. By attending to foam development proactively, suppliers can substantially improve production effectiveness and product top quality, ultimately adding to more cost-effective and lasting operations.
By recognizing the mechanisms of foam formation and picking ideal anti-foaming representatives, manufacturers can take positive actions to minimize too much foam. The attributes of the liquid tool, including thickness and density, further influence foam actions; why not try these out for instance, even more viscous liquids often tend to trap air much more properly, leading to increased foam stability.
Understanding these fundamental facets of foam formation is important for effective foam control in chemical manufacturing. By assessing historical foam information and functional specifications, these systems can forecast foam generation patterns and suggest preemptive actions. Foam Control. Normal audits of foam control gauges make sure that procedures remain optimized, while promoting a culture of aggressive foam administration can lead to sustainable enhancements across the production spectrum
Report this page